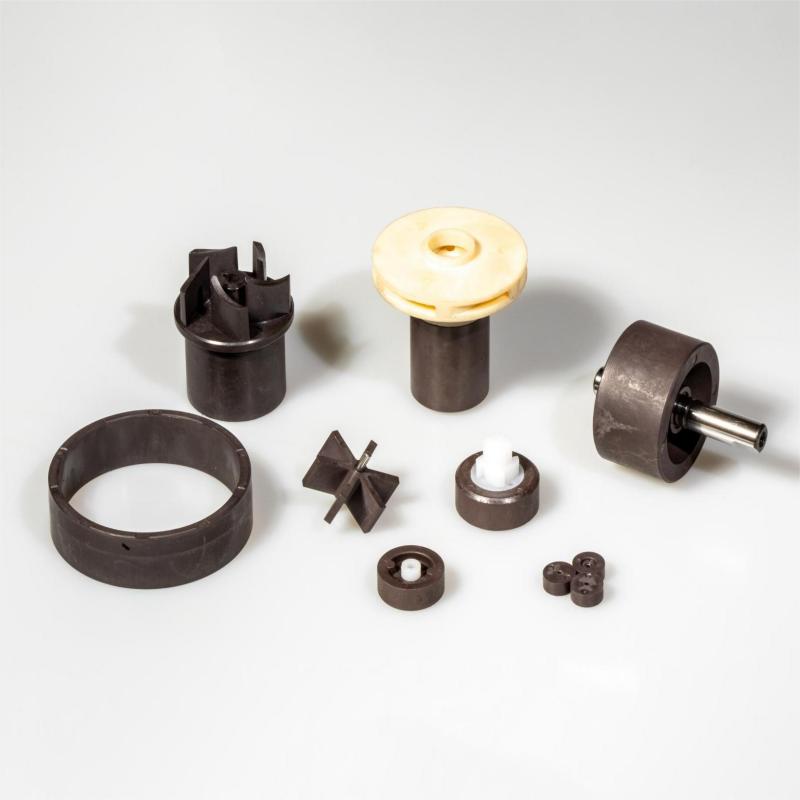
Injection-molded magnets provide almost unlimited dimensional and magnetic flexibility. Made by blending magnetic materials (NdFeB, ferrite) with a polymer binder (typically nylon or PPS), these magnets can be molded just like plastic. They enable complex shapes and can be directly over-molded onto components like shafts or bushings, often removing the need for additional gluing or assembly. Injection molding is ideal for applications requiring high precision, complex shapes, and insert or over-molding. This process enables the rapid production of identical components, making it well-suited for high-volume manufacturing. Injection molded magnets are commonly used in magnetic sensors, brakes, and other applications. Exceptional tensile strength ensures high resistance to impact and rotational forces, along with excellent chemical resistance.
| ∇ Versatile shapes and magnetization options |
| ∇ NdFeB, SmCo, AlNiCo, and Ferrite materials available |
| ∇ Ideal for large-scale applications |
| ∇ High resistance to impact, rotational forces, and chemicals |
| ∇ Maintain tight tolerances for precision |
Properties of Injection-molded Magnets
| Pa12 Series | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grade | TP-A19 | TP-A24 | TP-A25 | TP-F26CB | TP-A26NK | TP-F26S | TP-T27D | TP-A27E (PaA) | TP-A27E (P2A) ND2 | TP-A27E (SD) | TP-A27ES | TPA-202 | TP-A27E | TP-A27EC | TP-A27E(T) | TP-A27NK | TP-NK2 | TP-A27P | ||||
|
Magnetic Properties |
TODA NO.610-1 |
Residual Magnetic Beam Density | Br | mT (G) | 207 (2065) | 260 (2596) | 278 (2780) | 277 (2770) | 287 (2871) | 282 (2820) | 290 (2900) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2887) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2930) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2932) | 294 (2940) | 298 (2980) | 304 (3042) | 308 (3080) |
| Coercive Force | bHc | kA/m (Oe) | 160 (2003) | 185 (2328) | 190 (2386) | 186 (2341) | 189 (2370) | 188 (2353) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2402) | 187 (2350) | 194 (2430) | 192 (2410) | 190 (2390) | 187 (2335) | 191 (2400) | 197 (2480) | 185 (2322) | 183 (2300) | ||
| Intrinsic Coercivity | iHc | kA/m (Oe) | 248 (3118) | 242 (3038) | 238 (2985) | 233 (2926) | 231 (2907) | 228 (2870) | 230 (2890) | 239 (3000) | 232 (2912) | 229 (2880) | 234 (2940) | 231 (2900) | 229 (2880) | 228 (2852) | 231 (2900) | 235 (2950) | 216 (2711) | 211 (2650) | ||
| Maximum Magnetic Energy Product | (BH) max | kJ/m3 (MGOe) | 8.5 (1.058) | 13.4 (1.672) | 15.2 (1.902) | 15.2 (1.896) | 16.3 (2.038) | 15.6 (1.960) | 16.6 (2.080) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.5 (2.062) | 16.3 (2.050) | 16.5 (2.070) | 16.9 (2.130) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.8 (2.109) | 17.0 (2.140) | 17.4 (2.185) | 18.2 (2.275) | 18.8 (2.35) | ||
|
Physical Properties |
ASTM-D792 | Molding Density | g/cm3 | 2.90 | 3.40 | 3.57 | 3.55 | 3.63 | 3.63 | 3.64 | 3.65 | 3.65 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.69 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.74 | 3.78 | 3.82 | |
| ASTM-D1238 | Fluidity | MI | g/10min | 380 270°C/ 10kg |
163 |
34 |
70 |
150 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
100 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
40 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
63 270°C/ 10kg |
58 270°C/ 10kg |
85 270°C/ 10kg |
75 270°C/ 10kg |
76 270°C/ 10kg |
|
| Condition | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASTM-D790 | Bending Strength | MPa | 119 | 100 | 122 | 112 | 103 | 115 | 96 | 111 | 110 | 92 | 104 | 113 | 92 | 92 | 105 | 99 | 114 | 110 | ||
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | 6.9 | 9.7 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 12.0 | 14.5 | 10.9 | 11.5 | 10.6 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 13.3 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 14.3 | 19.3 | |||
| ASTM-D638 | Tensile Strength | MPa | 63 | 54 | 66 | 61 | 54 | 59 | 49 | 51 | 52 | 46 | 54 | 58 | 46 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 52 | 67 | ||
| Stretch | % | 6.0 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 5.3 | 4.9 | 4.0 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.7 | |||
| ASTM-D256 | 1ZOD Impact Strength | kJ/m2 | NB | 20.9 | 23.1 | 19.9 | 12.3 | 15.6 | 16.5 | 21.4 | 23.1 | 20.4 | 20.1 | 17.6 | 20.4 | 18.0 | 21.6 | 12.1 | 12.3 | 11.0 | ||
| Toda | Skrinkage | % | 1.05 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.48 | ||
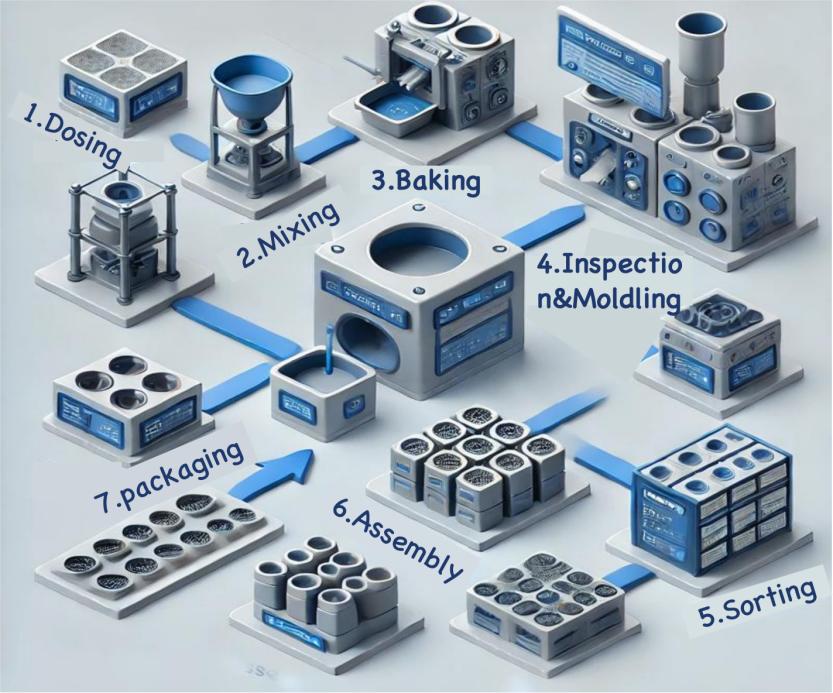
Demagnetization Curves of Injection-molded magnets at Different Temperatures
Process Flow