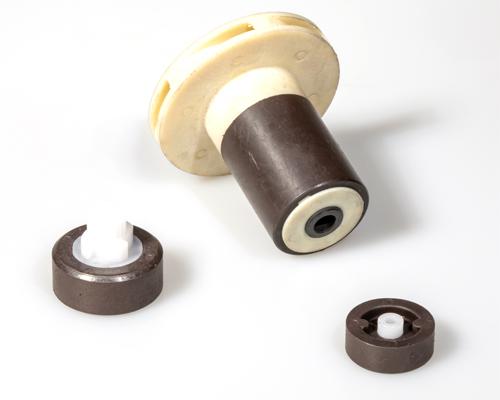

Integrated assemblies injection molded magnets are engineered to provide precise, reliable magnetic performance directly within complex systems. Manufactured by combining magnetic powders with polymer binders through an injection molding process, these magnets are embedded within custom assemblies to reduce the need for additional components and streamline product designs. Ideal for use in applications requiring high accuracy and consistency, integrated assemblies injection molded magnets are often found in automotive systems, sensors, medical devices, and industrial machinery.
At ZOYN, we specialize in creating integrated assemblies injection molded magnets tailored to meet the specific needs of diverse industries, including automotive, medical, electronics, and automation. Our expertise in advanced design and manufacturing ensures high-performance magnetic solutions with seamless integration and durability for even the most demanding applications.
Key Features of Integrated Assemblies Injection Molded Magnets
1. Customized Magnetization: Can be magnetized in axial, radial, or multipole configurations to suit specific application needs, ensuring precise control of magnetic fields.
2. High Precision and Tight Tolerances: Injection molding allows for exact shaping, creating magnets that meet tight tolerances for seamless integration into assemblies.
3. Lightweight and Durable: The polymer-binder composite structure reduces weight while maintaining durability, ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
4. Corrosion Resistance: Naturally resistant to rust, moisture, and harsh environments; optional coatings such as epoxy or nickel can be added for extra protection.
5. Space-Saving Design: Integrated assemblies simplify product designs by embedding the magnet directly into the structure, reducing component count and assembly time.
6. Cost-Efficient Manufacturing: The injection molding process enables economical production of intricate shapes, ideal for complex and high-volume applications.
7. Temperature Resistance: Available in specialized grades for high-temperature environments, ensuring consistent performance in extreme conditions.
Injection Molded Magnets's Manufacturing Process
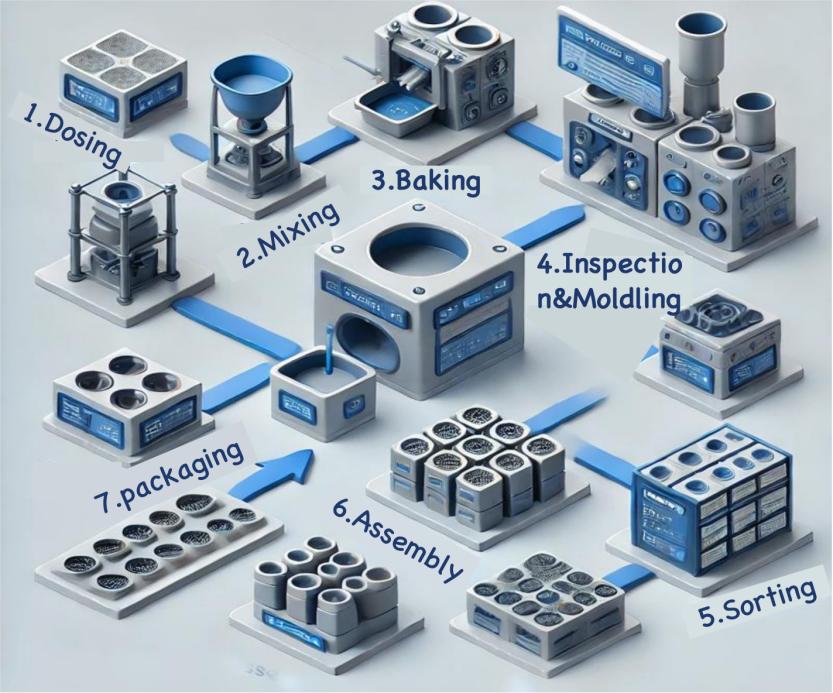
Main Applications
Properties of Injection-Molded Ferrites
| Pa12 Series | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grade | TP-A19 | TP-A24 | TP-A25 | TP-F26CB | TP-A26NK | TP-F26S | TP-T27D | TP-A27E (PaA) | TP-A27E (P2A) ND2 | TP-A27E (SD) | TP-A27ES | TPA-202 | TP-A27E | TP-A27EC | TP-A27E(T) | TP-A27NK | TP-NK2 | TP-A27P | ||||
|
Magnetic Properties |
TODA NO.610-1 |
Residual Magnetic Beam Density | Br | mT (G) | 207 (2065) | 260 (2596) | 278 (2780) | 277 (2770) | 287 (2871) | 282 (2820) | 290 (2900) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2887) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2930) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2932) | 294 (2940) | 298 (2980) | 304 (3042) | 308 (3080) |
| Coercive Force | bHc | kA/m (Oe) | 160 (2003) | 185 (2328) | 190 (2386) | 186 (2341) | 189 (2370) | 188 (2353) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2402) | 187 (2350) | 194 (2430) | 192 (2410) | 190 (2390) | 187 (2335) | 191 (2400) | 197 (2480) | 185 (2322) | 183 (2300) | ||
| Intrinsic Coercivity | iHc | kA/m (Oe) | 248 (3118) | 242 (3038) | 238 (2985) | 233 (2926) | 231 (2907) | 228 (2870) | 230 (2890) | 239 (3000) | 232 (2912) | 229 (2880) | 234 (2940) | 231 (2900) | 229 (2880) | 228 (2852) | 231 (2900) | 235 (2950) | 216 (2711) | 211 (2650) | ||
| Maximum Magnetic Energy Product | (BH) max |
kJ/m3 (MGOe) |
8.5 (1.058) | 13.4 (1.672) | 15.2 (1.902) | 15.2 (1.896) | 16.3 (2.038) | 15.6 (1.960) | 16.6 (2.080) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.5 (2.062) | 16.3 (2.050) | 16.5 (2.070) | 16.9 (2.130) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.8 (2.109) | 17.0 (2.140) | 17.4 (2.185) | 18.2 (2.275) | 18.8 (2.35) | ||
|
Physical Properties |
ASTM-D792 | Molding Density | g/cm3 | 2.90 | 3.40 | 3.57 | 3.55 | 3.63 | 3.63 | 3.64 | 3.65 | 3.65 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.69 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.74 | 3.78 | 3.82 | |
| ASTM-D1238 | Fluidity | MI | g/10min | 380 270°C/ 10kg |
163 |
34 |
70 |
150 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
100 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
40 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
63 270°C/ 10kg |
58 270°C/ 10kg |
85 270°C/ 10kg |
75 270°C/ 10kg |
76 270°C/ 10kg |
|
| Condition | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASTM-D790 | Bending Strength | MPa | 119 | 100 | 122 | 112 | 103 | 115 | 96 | 111 | 110 | 92 | 104 | 113 | 92 | 92 | 105 | 99 | 114 | 110 | ||
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | 6.9 | 9.7 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 12.0 | 14.5 | 10.9 | 11.5 | 10.6 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 13.3 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 14.3 | 19.3 | |||
| ASTM-D638 | Tensile Strength | MPa | 63 | 54 | 66 | 61 | 54 | 59 | 49 | 51 | 52 | 46 | 54 | 58 | 46 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 52 | 67 | ||
| Stretch | % | 6.0 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 5.3 | 4.9 | 4.0 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.7 | |||
| ASTM-D256 | 1ZOD Impact Strength | kJ/m2 | NB | 20.9 | 23.1 | 19.9 | 12.3 | 15.6 | 16.5 | 21.4 | 23.1 | 20.4 | 20.1 | 17.6 | 20.4 | 18.0 | 21.6 | 12.1 | 12.3 | 11.0 | ||
| Toda | Skrinkage | % | 1.05 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.48 | ||