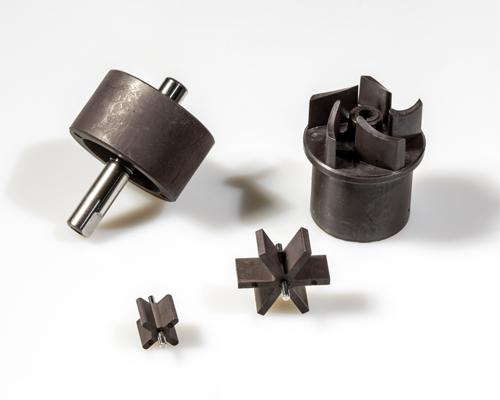
Rotor injection molded magnets are specially designed to deliver precise and powerful magnetic fields in rotary applications, enhancing the performance and efficiency of motors and other rotating machinery. Manufactured by combining high-performance magnetic powders with polymer binders through an injection molding process, these magnets allow for complex shapes, tight tolerances, and custom magnetization patterns. Ideal for use in electric motors, generators, and automotive systems, rotor injection molded magnets ensure smooth and consistent operation even under demanding conditions.
At ZOYN, we specialize in producing high-quality rotor injection molded magnets tailored to meet the unique needs of industries such as automotive, renewable energy, industrial automation, and robotics. With advanced manufacturing capabilities, customizable configurations, and durable materials, our magnets provide the strength, precision, and reliability needed for efficient rotary systems.
1. Customized Magnetization Patterns
Can be magnetized in axial, radial, or multipole configurations, allowing for precise control of magnetic fields for specific motor requirements.
2. High Precision and Tight Tolerances
Injection molding allows for exact shaping, resulting in magnets that meet tight tolerances and fit seamlessly within rotor assemblies.
3. Lightweight and Compact Design
The polymer-binder composite structure reduces weight without sacrificing strength, making these magnets ideal for compact, high-speed applications.
4. Corrosion Resistance
Naturally resistant to moisture and rust, with optional protective coatings (such as epoxy or nickel) available for additional durability in challenging environments.
5. Temperature Stability
Available in specialized grades for high-temperature applications, ensuring reliable performance in demanding conditions.
6. Cost-Effective Production
The injection molding process enables economical manufacturing, especially for intricate designs and high-volume orders.
7. Enhanced Magnetic Performance
Delivers consistent magnetic fields and high magnetic strength, essential for efficient and stable rotary operation.
Properties of Injection-Molded Ferrites
| Pa12 Series | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grade | TP-A19 | TP-A24 | TP-A25 | TP-F26CB | TP-A26NK | TP-F26S | TP-T27D | TP-A27E (PaA) | TP-A27E (P2A) ND2 | TP-A27E (SD) | TP-A27ES | TPA-202 | TP-A27E | TP-A27EC | TP-A27E(T) | TP-A27NK | TP-NK2 | TP-A27P | ||||
|
Magnetic Properties |
TODA NO.610-1 |
Residual Magnetic Beam Density | Br | mT (G) | 207 (2065) | 260 (2596) | 278 (2780) | 277 (2770) | 287 (2871) | 282 (2820) | 290 (2900) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2887) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2930) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2932) | 294 (2940) | 298 (2980) | 304 (3042) | 308 (3080) |
| Coercive Force | bHc | kA/m (Oe) | 160 (2003) | 185 (2328) | 190 (2386) | 186 (2341) | 189 (2370) | 188 (2353) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2402) | 187 (2350) | 194 (2430) | 192 (2410) | 190 (2390) | 187 (2335) | 191 (2400) | 197 (2480) | 185 (2322) | 183 (2300) | ||
| Intrinsic Coercivity | iHc | kA/m (Oe) | 248 (3118) | 242 (3038) | 238 (2985) | 233 (2926) | 231 (2907) | 228 (2870) | 230 (2890) | 239 (3000) | 232 (2912) | 229 (2880) | 234 (2940) | 231 (2900) | 229 (2880) | 228 (2852) | 231 (2900) | 235 (2950) | 216 (2711) | 211 (2650) | ||
| Maximum Magnetic Energy Product | (BH) max |
kJ/m3 (MGOe) |
8.5 (1.058) | 13.4 (1.672) | 15.2 (1.902) | 15.2 (1.896) | 16.3 (2.038) | 15.6 (1.960) | 16.6 (2.080) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.5 (2.062) | 16.3 (2.050) | 16.5 (2.070) | 16.9 (2.130) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.8 (2.109) | 17.0 (2.140) | 17.4 (2.185) | 18.2 (2.275) | 18.8 (2.35) | ||
|
Physical Properties |
ASTM-D792 | Molding Density | g/cm3 | 2.90 | 3.40 | 3.57 | 3.55 | 3.63 | 3.63 | 3.64 | 3.65 | 3.65 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.69 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.74 | 3.78 | 3.82 | |
| ASTM-D1238 | Fluidity | MI | g/10min | 380 270°C/ 10kg |
163 |
34 |
70 |
150 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
100 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
40 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
63 270°C/ 10kg |
58 270°C/ 10kg |
85 270°C/ 10kg |
75 270°C/ 10kg |
76 270°C/ 10kg |
|
| Condition | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASTM-D790 | Bending Strength | MPa | 119 | 100 | 122 | 112 | 103 | 115 | 96 | 111 | 110 | 92 | 104 | 113 | 92 | 92 | 105 | 99 | 114 | 110 | ||
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | 6.9 | 9.7 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 12.0 | 14.5 | 10.9 | 11.5 | 10.6 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 13.3 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 14.3 | 19.3 | |||
| ASTM-D638 | Tensile Strength | MPa | 63 | 54 | 66 | 61 | 54 | 59 | 49 | 51 | 52 | 46 | 54 | 58 | 46 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 52 | 67 | ||
| Stretch | % | 6.0 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 5.3 | 4.9 | 4.0 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.7 | |||
| ASTM-D256 | 1ZOD Impact Strength | kJ/m2 | NB | 20.9 | 23.1 | 19.9 | 12.3 | 15.6 | 16.5 | 21.4 | 23.1 | 20.4 | 20.1 | 17.6 | 20.4 | 18.0 | 21.6 | 12.1 | 12.3 | 11.0 | ||
| Toda | Skrinkage | % | 1.05 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.48 | ||
Process Flow