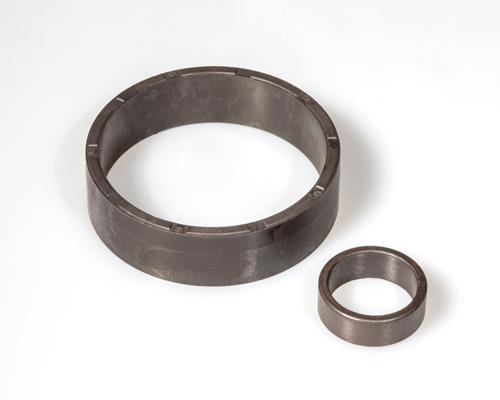
Injection Molded Ring Magnets are a highly versatile magnetic solution, engineered for precision and adaptability in advanced applications. These magnets are crafted using a specialized injection molding process that combines magnetic powders with polymer binders, allowing for intricate shapes and custom magnetization patterns. Their ring shape is particularly suited for rotary applications, such as motors, sensors, and encoders, where consistent and reliable magnetic performance is critical.
At ZOYN, we produce high-quality injection molded ring magnets tailored to meet the unique demands of industries such as automotive, robotics, electronics, and renewable energy. Whether you need multipole magnetization, custom dimensions, or integration with other components, our magnets deliver exceptional performance and durability in even the most challenging environments.
1. Customizable Magnetization
Rings can be magnetized in various orientations, including radially, axially, or in multipole configurations, to meet specific application requirements.
2. Complex Geometries
Injection molding allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances, enabling the production of highly customized magnets that fit seamlessly into advanced systems.
3. Durability and Stability
These magnets maintain their magnetic properties over time and are resistant to corrosion, vibration, and thermal stress, ensuring long-term reliability.
4. Integration-Ready Designs
Injection molded ring magnets can be over-molded or combined with shafts, gears, and other components during the manufacturing process, simplifying assembly and improving product performance.
5. Lightweight and Strong
The combination of magnetic materials and polymers results in a lightweight yet strong magnet, ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial.
6. Cost-Effective
Compared to sintered magnets, injection molded ring magnets are more economical for producing complex shapes or high-precision components in large quantities.
Properties of Injection-Molded Ferrites
| Pa12 Series | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Grade | TP-A19 | TP-A24 | TP-A25 | TP-F26CB | TP-A26NK | TP-F26S | TP-T27D | TP-A27E (PaA) | TP-A27E (P2A) ND2 | TP-A27E (SD) | TP-A27ES | TPA-202 | TP-A27E | TP-A27EC | TP-A27E(T) | TP-A27NK | TP-NK2 | TP-A27P | ||||
|
Magnetic Properties |
TODA NO.610-1 |
Residual Magnetic Beam Density | Br | mT (G) | 207 (2065) | 260 (2596) | 278 (2780) | 277 (2770) | 287 (2871) | 282 (2820) | 290 (2900) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2887) | 288 (2880) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2930) | 289 (2890) | 293 (2932) | 294 (2940) | 298 (2980) | 304 (3042) | 308 (3080) |
| Coercive Force | bHc | kA/m (Oe) | 160 (2003) | 185 (2328) | 190 (2386) | 186 (2341) | 189 (2370) | 188 (2353) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2400) | 191 (2402) | 187 (2350) | 194 (2430) | 192 (2410) | 190 (2390) | 187 (2335) | 191 (2400) | 197 (2480) | 185 (2322) | 183 (2300) | ||
| Intrinsic Coercivity | iHc | kA/m (Oe) | 248 (3118) | 242 (3038) | 238 (2985) | 233 (2926) | 231 (2907) | 228 (2870) | 230 (2890) | 239 (3000) | 232 (2912) | 229 (2880) | 234 (2940) | 231 (2900) | 229 (2880) | 228 (2852) | 231 (2900) | 235 (2950) | 216 (2711) | 211 (2650) | ||
| Maximum Magnetic Energy Product | (BH) max |
kJ/m3 (MGOe) |
8.5 (1.058) | 13.4 (1.672) | 15.2 (1.902) | 15.2 (1.896) | 16.3 (2.038) | 15.6 (1.960) | 16.6 (2.080) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.5 (2.062) | 16.3 (2.050) | 16.5 (2.070) | 16.9 (2.130) | 16.4 (2.060) | 16.8 (2.109) | 17.0 (2.140) | 17.4 (2.185) | 18.2 (2.275) | 18.8 (2.35) | ||
|
Physical Properties |
ASTM-D792 | Molding Density | g/cm3 | 2.90 | 3.40 | 3.57 | 3.55 | 3.63 | 3.63 | 3.64 | 3.65 | 3.65 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 3.69 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.74 | 3.78 | 3.82 | |
| ASTM-D1238 | Fluidity | MI | g/10min | 380 270°C/ 10kg |
163 |
34 |
70 |
150 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
100 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
40 270°C/ 10kg |
60 270°C/ 10kg |
65 270°C/ 10kg |
63 270°C/ 10kg |
58 270°C/ 10kg |
85 270°C/ 10kg |
75 270°C/ 10kg |
76 270°C/ 10kg |
|
| Condition | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASTM-D790 | Bending Strength | MPa | 119 | 100 | 122 | 112 | 103 | 115 | 96 | 111 | 110 | 92 | 104 | 113 | 92 | 92 | 105 | 99 | 114 | 110 | ||
| Flexural Modulus | GPa | 6.9 | 9.7 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 12.0 | 14.5 | 10.9 | 11.5 | 10.6 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 13.3 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 12.5 | 15.1 | 14.3 | 19.3 | |||
| ASTM-D638 | Tensile Strength | MPa | 63 | 54 | 66 | 61 | 54 | 59 | 49 | 51 | 52 | 46 | 54 | 58 | 46 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 52 | 67 | ||
| Stretch | % | 6.0 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 5.3 | 4.9 | 4.0 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.7 | |||
| ASTM-D256 | 1ZOD Impact Strength | kJ/m2 | NB | 20.9 | 23.1 | 19.9 | 12.3 | 15.6 | 16.5 | 21.4 | 23.1 | 20.4 | 20.1 | 17.6 | 20.4 | 18.0 | 21.6 | 12.1 | 12.3 | 11.0 | ||
| Toda | Skrinkage | % | 1.05 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.55 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.48 | ||
Process Flow